Three Diabetes Facts You Need To Know

Did you know that someone in the United States is diagnosed with diabetes every 19 seconds? This condition affects nearly 30 million children and adults in the U.S. today – that’s nearly 10 percent of the population.
Despite the prevalence of diabetes, many don’t know the risk factors and warning signs to be aware of. In honor of Diabetes Awareness Month, here are three things you need to know about diabetes.
1. There are three types of diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes is also known as Juvenile Diabetes or Insulin-Dependent Diabetes. In this type of diabetes, your body no longer makes insulin or enough insulin. Without it, cells cannot absorb glucose, which they need to produce energy.
Treatment may include taking insulin injections, making healthy food choices, being physically active, and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Type 2 Diabetes
If you have Type 2 Diabetes, your body experiences insulin resistance. This means your body does not use insulin properly; at first, your pancreas will make extra insulin to compensate. However, your body will not be able to continue producing enough insulin to keep your blood glucose levels normal. This is known as insulin deficiency.
Type 2 Diabetes is the most common form of diabetes; it makes up approximately 90% of all cases worldwide. While this form of diabetes can affect people of any age, it develops most often in middle-aged and older adults. Obesity and physical inactivity are prominent risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes.
Treatment may include taking medication, making healthy food choices, being physically active and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes can develop during pregnancy due to the production of hormones that lead to insulin resistance.
Untreated or poorly controlled gestational diabetes can affect not only the mother, but also the baby. Due to high insulin levels, the baby may have low blood glucose levels, higher risk for breathing problems, and increased risk of obesity later in life.
Typically, expectant moms can control gestational diabetes through healthy eating, regular exercise and medication. Although this condition often goes away later in life, a woman who has had gestational diabetes is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life. The same is true of children born to mothers who had this condition.
2. Diabetes is a costly chronic condition.
The total national cost of diagnosed diabetes in the U.S. is an estimated $245 billion. This infographic from the American Diabetes Association breaks down how money is spent on the care and treatment for diabetes.
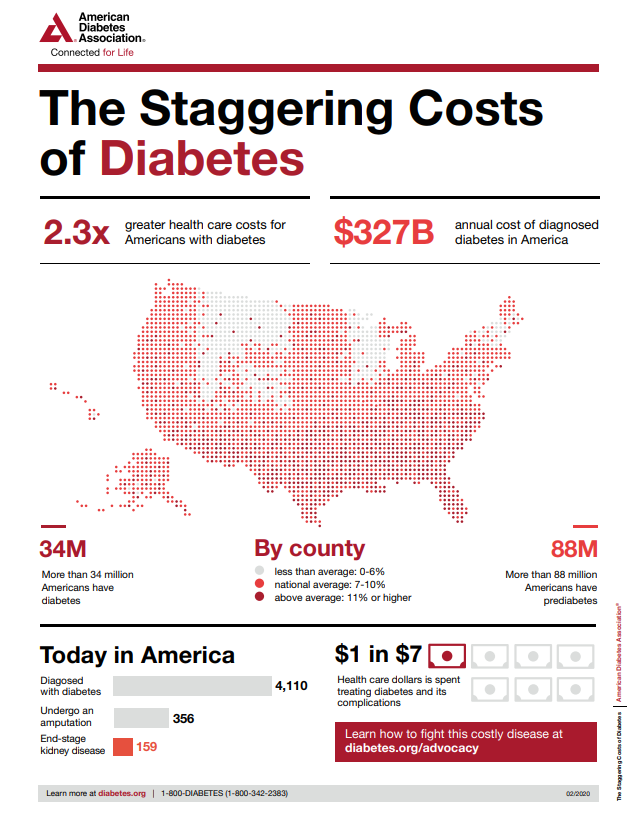
Courtesy of the American Diabetes Association
3. Diabetes is one of the top disabling conditions in the United States.
Most people with diabetes can manage their condition through medication and monitoring what they eat. However, diabetes can sometimes lead to disabling illnesses and injuries that prevent you from working.
Unfortunately, disability claims filed by people with diabetes are often denied, even if they are truly unable to work. Diabetes is not automatically considered a disability under Social Security Administration guidelines, but is individually evaluated based on its impact on the rest of the body. Work-sponsored short or long term disability plans all have different definitions of disability, so read your policy closely to learn more.
If you have questions about obtaining disability benefits due to a diabetes diagnosis, contact a top-rated disability attorney for a free consultation.


